A cloud backup is a type of backup solution that involves copying and storing data on a remote server or servers, which are typically owned and managed by a third-party cloud storage provider. Cloud backups are accessed over the internet, and are intended to protect data from loss due to events such as hardware failure, theft, natural disasters, or cyberattacks.

How Cloud Backups Work
The cloud backup process typically works by following the steps below:
- Data is selected for backup: This can include files, databases, applications, and other digital assets.
- The data is compressed and encrypted: This is done to reduce the amount of storage space required and to protect the data from unauthorized access.
- The data is transferred to a remote server: This is done over an internet connection, usually using a secure protocol such as HTTPS or FTPS.
- The data is stored on the remote server: The data is usually stored across multiple servers for redundancy and may be distributed across multiple geographic locations to improve reliability.
- The data can be accessed and restored as needed: Users can usually access their cloud backups through a web interface or client software and can restore their data to its original location or to a new device as needed.
Cloud backups involve storing data on remote servers accessible via the internet, providing a secure and off-site location for data preservation. This process starts with the selection of data to be backed up, which can range from files and folders to entire systems and databases. Once selected, this data is encrypted to ensure its security during transmission and while stored on the cloud servers. Encryption is a critical step, utilizing algorithms to convert data into a format that can be decoded only with a decryption key, thereby safeguarding the data from unauthorized access.
The transmission of data to cloud servers utilizes internet protocols, such as the Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS), to maintain a secure connection and protect the data from interception or tampering during transfer. Upon reaching the cloud servers, the data is stored across multiple locations to ensure redundancy. This redundancy is crucial for data recovery in case of a server failure, providing multiple copies of the data across different physical locations. Cloud providers often use data centers spread across various geographic locations to enhance this aspect of data security and availability.
Data deduplication is another technical aspect of cloud backups, aimed at optimizing storage requirements and reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the internet. By identifying and eliminating duplicate copies of data before transmission, deduplication not only conserves bandwidth but also reduces storage costs on the cloud provider’s infrastructure.
Backup scheduling and versioning are features that allow for automatic and periodic backups, ensuring that data is continually updated on the cloud servers. This scheduling can be configured to meet specific needs, such as daily, weekly, or real-time backups, providing flexibility and ensuring that recent data changes are captured. Versioning keeps multiple versions of files, allowing users to restore data from a specific point in time, which is especially useful in scenarios such as data corruption or accidental deletion.
Cloud backups also employ compression techniques to reduce the size of the data being backed up, further conserving bandwidth and reducing storage space requirements on the cloud. Compression algorithms work by identifying and eliminating redundancy within the data without losing information, making the backup process more efficient.
Monitoring and management tools provided by cloud backup services offer insights into the backup process, including the status of ongoing or completed backups, data usage statistics, and any issues encountered during the backup process. These tools are essential for maintaining the integrity of the backup process and ensuring that data is accurately and securely backed up to the cloud servers.
Device and Operating System Compatibility with Cloud Backups
Most modern devices can utilize cloud backups, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, desktop computers, and even servers. Here are some examples of specific devices and platforms that support cloud backups:
- Mobile devices: Android and iOS devices such as smartphones and tablets can use cloud backup services like Google Drive, iCloud, or OneDrive to back up their data, including contacts, photos, messages, and app data.
- Computers: Windows and macOS computers can use cloud backup services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive to back up their files, documents, and folders.
- Servers: Enterprise-level servers can use cloud backup services like Amazon S3, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Storage to back up their data and configurations.
Cloud backup services are designed to be widely compatible across a variety of devices and operating systems, ensuring broad accessibility and flexibility.
Desktop and Laptop Computers
On the desktop front, Windows and macOS are fully supported by most cloud backup providers. Windows compatibility typically spans several versions, including but not limited to Windows 10 and Windows 11, catering to both home and enterprise environments. macOS users, from Mojave to the latest releases, can also take advantage of cloud backup solutions, which integrate seamlessly with Apple’s ecosystem.
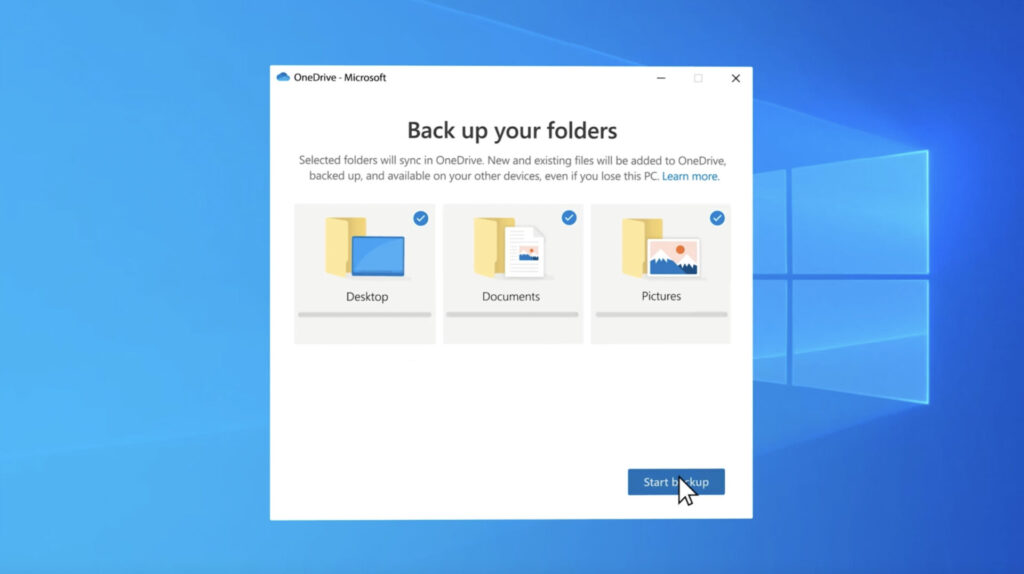
Linux support, while not as universal, is nonetheless available with several providers offering solutions tailored for popular distributions such as Ubuntu, CentOS, and Debian. This support ensures that servers and desktops running on open-source platforms can also leverage cloud backups for data protection.
Smartphones
Android and iOS are comprehensively supported, allowing for backup of contacts, photos, videos, and app data. Cloud backup apps for Android typically support a wide range of versions, from older iterations to the latest releases, ensuring that devices, regardless of their age, can back up data to the cloud. iOS support covers recent versions, enabling iPhone and iPad users to securely store their data off-site, with the process often deeply integrated into the device’s settings for convenience.
NAS Systems and Enterprise Servers
Specialized devices such as network-attached storage (NAS) systems and enterprise servers also benefit from cloud backup compatibility. NAS devices from manufacturers like Synology and QNAP have built-in support for cloud backup services, enabling both individual users and businesses to back up large volumes of data directly from their on-premises hardware to the cloud. For enterprise servers, cloud backup solutions often provide support for server operating systems like Windows Server and Linux-based servers, ensuring that critical business data and applications are protected.
Web Interfaces and APIs
Cloud backup services typically offer a variety of client software and apps tailored for specific operating systems and devices, ensuring an optimized backup experience. Additionally, many cloud backup providers offer web-based interfaces and APIs, allowing for custom integration and the ability to back up devices or systems that may not have dedicated support, thereby extending compatibility even further.
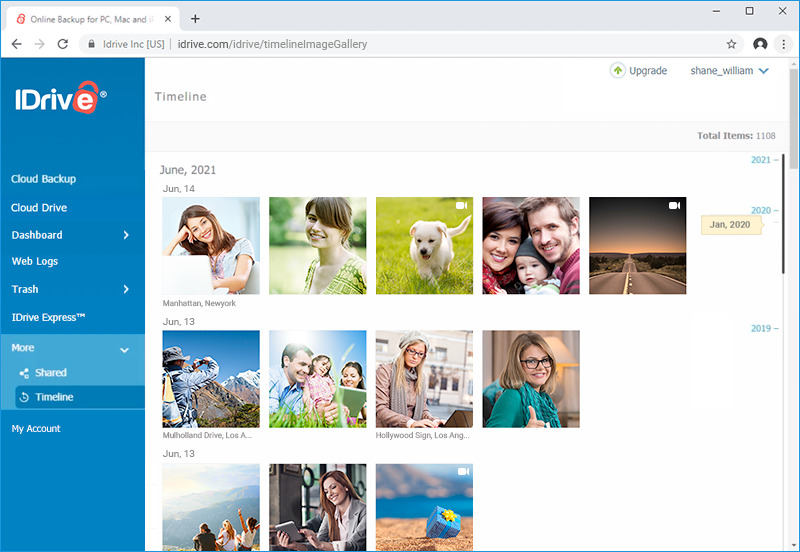
Encryption and Security
Encryption and security measures are consistent across devices and operating systems, ensuring that data is protected regardless of the platform. This universal approach to data security means that users can expect a high level of encryption, such as AES 256-bit, and secure transmission protocols, regardless of the device or operating system they are using.
Advantages of Cloud Backups
Cloud backups offer several advantages over other backup solutions, including:
- Accessibility: Cloud backups can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, making them ideal for remote workers or people who need to access their data on the go.
- Scalability: Cloud backups can be scaled up or down to accommodate changing storage needs, without the need to purchase additional hardware.
- Reliability: Cloud backups are usually stored across multiple servers for redundancy, which helps to ensure that data is available when needed.
- Security: Cloud backups are typically encrypted and stored in secure data centers, which can provide better security than on-premises backups.
Cloud backups offer a multitude of advantages that cater to the need for reliable, secure, and efficient data protection strategies. One of the primary benefits is the off-site storage of data, which ensures that critical information is safeguarded against local disasters such as fires, floods, or hardware failures. By storing data remotely, businesses and individuals can recover their information even if their physical infrastructure is compromised, providing a robust solution for disaster recovery.
Accessibility and convenience are significant advantages of cloud backups. Data stored in the cloud can be accessed from any location with an internet connection, offering flexibility for users who need to retrieve their information on the go or from different devices. This accessibility supports remote work environments and mobile users, ensuring that data is always within reach when needed.
Scalability is another key benefit, as cloud backup services allow users to easily adjust their storage requirements based on current needs. This flexibility means that businesses can expand their backup capacity as they grow, without the need for significant upfront investments in physical storage infrastructure. The pay-as-you-go model of many cloud services also allows for cost-effective scalability, where users only pay for the storage they use.
Cloud backups also offer enhanced security features, including encryption of data both in transit and at rest. Advanced encryption standards protect data from unauthorized access, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential. Moreover, cloud providers implement rigorous security protocols and compliance standards to safeguard data against cyber threats, providing an added layer of protection for users’ information.
Automated backup processes simplify the task of data protection, reducing the risk of human error and ensuring that data is regularly backed up without the need for manual intervention. Users can set backup schedules that automatically protect their data at regular intervals, providing peace of mind that their information is up-to-date and secure.
Version control is an essential feature of cloud backups, allowing users to save multiple versions of their files. This capability is invaluable for recovering from accidental deletions or restoring earlier versions of documents, providing a safety net that enhances data integrity and recovery options.
Data deduplication technology, used in cloud backups, optimizes storage efficiency by eliminating redundant copies of data. This process reduces the amount of data that needs to be transferred and stored, leading to faster backup times and lower storage costs.
Cloud Backups vs Local Backups
A local backup refers to backing up data to a storage device that is physically located nearby, such as an external hard drive or a USB drive. In contrast, a cloud backup refers to backing up data to a remote server that is accessed over the internet.
Here are some of the key differences between local backups and cloud backups using some of the criteria mentioned in the earlier section:
- Location: Local backups are stored on physical storage devices that are typically located near the computer or device being backed up, while cloud backups are stored on remote servers that are accessed over the internet.
- Accessibility: Local backups are only accessible if the storage device is physically connected to the computer or device being restored, while cloud backups can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
- Security: Local backups are vulnerable to physical damage or theft, and may not be encrypted by default, whereas cloud backups are generally more secure due to being stored on remote servers that are usually encrypted.
- Scalability: Local backups may have limitations on storage capacity, while cloud backups can be scaled up to accommodate larger amounts of data.
- Cost: Local backups generally require the purchase of physical storage devices, which can add up over time, while cloud backups typically require a subscription fee for the storage space and services provided.
Cloud backup involves storing data on servers located in remote data centers, accessible over the internet. This method provides off-site storage that is managed by third-party service providers, offering benefits such as scalability, remote access, and disaster recovery capabilities. Data stored in the cloud is protected through encryption, both in transit and at rest, ensuring security against unauthorized access. Cloud backups are typically automated and can be scheduled to occur at regular intervals, providing up-to-date protection of data without manual intervention. The pay-as-you-go pricing model of cloud services allows for cost-effective scalability, enabling users to adjust their storage needs as required without significant upfront investments.
Local backup, on the other hand, involves storing data on physical devices or media within the user’s premises, such as external hard drives, USB drives, NAS (Network Attached Storage) devices, or even on the local network. This method offers fast access to backed-up data since it is stored on-site and does not require an internet connection for data retrieval. Local backups provide users with full control over their backup infrastructure and data, allowing for customized backup solutions tailored to specific needs. However, local backups require upfront investment in hardware and storage media, and the responsibility for the security and maintenance of the backup devices lies with the user. Unlike cloud backups, local backups are susceptible to physical damage or loss due to disasters such as fires, floods, or theft, which can result in the loss of both original and backup data.

The key difference between cloud backups and local backups lies in their approach to storing and managing data. Cloud backups offer a hands-off, scalable solution with off-site data protection, ideal for ensuring data availability even in the event of a local disaster. Local backups, while providing quicker access and control over the backup process, require more hands-on management and are vulnerable to local environmental risks. The choice between cloud and local backups often depends on specific needs, including data security requirements, accessibility, budget constraints, and the importance of maintaining control over the backup infrastructure.
Why is it Important to Backup Data?
Backing up data to the cloud is important for several reasons:
- Protection against data loss: Cloud backups can protect against data loss due to events such as hardware failure, theft, natural disasters, or cyberattacks. By storing data in a remote location, users can ensure that their data is protected from local events that could otherwise destroy it.
- Accessibility: Cloud backups can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection, making it easy for users to retrieve their data even if they are away from their usual device.
- Scalability: Cloud backups can be scaled up or down to accommodate changing storage needs, without the need to purchase additional hardware.
- Redundancy: Cloud backups are usually stored across multiple servers for redundancy, which helps to ensure that data is available when needed.
- Security: Cloud backups are typically encrypted and stored in secure data centers, which can provide better security than on-premises backups.
- Automatic backups: Cloud backup solutions often provide automatic backups, which can ensure that data is backed up regularly without requiring users to manually initiate the backup process.
Backing up data is crucial for ensuring the continuity of operations and the integrity of information in both personal and professional contexts. Data loss can occur due to various reasons, including hardware failures, software corruption, human error, cyber-attacks, and natural disasters. Without backups, recovering lost data might be impossible, leading to significant consequences such as operational downtime, financial loss, legal implications, and damage to reputation.
Data backups enable quick recovery from data loss incidents, minimizing downtime and ensuring that critical information remains accessible. This is particularly important for businesses, where data availability is directly linked to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. In environments where data is constantly being updated, such as databases and customer records, regular backups ensure that recent changes are not lost, maintaining the accuracy and relevance of the data.
Backups act as a safety net against ransomware attacks. These attacks encrypt data, rendering it inaccessible without payment of a ransom. However, with up-to-date backups, organizations can restore their data without capitulating to the demands of cybercriminals, thereby mitigating the impact of the attack.
Backing up data also aids in compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. Many industries are subject to regulations that mandate the protection and retention of data for specified periods. Regular backups ensure that organizations can meet these requirements, avoiding legal penalties and ensuring that they can respond to audits, litigation, and inquiries effectively.
Data backups play a pivotal role in disaster recovery planning. By having backups stored off-site or in the cloud, organizations can recover their data even in the event of a total loss at the primary site, such as in the case of a natural disaster. This capability is essential for maintaining business continuity under adverse conditions.
Backups protect against the loss of irreplaceable items such as photographs, documents, and personal projects. The sentimental or intrinsic value of such data often surpasses its monetary worth, highlighting the importance of regular backups to safeguard personal memories and achievements.
Cloud Backups and Identity Theft Protection
Cloud backups can help protect against identity theft in a few ways:
- Securing personal information: By storing important personal information, such as financial records and sensitive documents, in encrypted cloud backups, individuals can ensure that their information is protected against unauthorized access. This helps to prevent hackers from stealing the information and using it to commit identity theft.
- Providing backup copies: If an individual’s computer or mobile device is lost, stolen, or damaged, they may lose access to important personal information. By backing up their data to the cloud, individuals can easily retrieve their data from another device, which reduces the risk of identity theft due to lost or stolen devices.
- Enabling remote access: Cloud backups can allow users to remotely access their data from anywhere with an internet connection. This means that if an individual is traveling or away from their usual device, they can still access their information securely, reducing the risk of identity theft.
- Providing version control: In the event that personal information is compromised, cloud backups can provide a history of changes made to files, enabling users to revert to a previous version before the compromise occurred.
Cloud backups protect against identity theft by ensuring that personal and sensitive data is securely stored and easily recoverable in the event of data breaches or loss. Identity theft often occurs through unauthorized access to personal information, such as social security numbers, financial records, or personal identification documents. When such data is lost or stolen from personal devices or compromised systems, it can lead to identity theft. Cloud backups mitigate this risk through several key security measures.
Encryption is the first line of defense in protecting data stored in cloud backups. By encrypting data both during transmission to the cloud and while at rest on cloud servers, cloud backup services ensure that personal information is unreadable to unauthorized individuals. Advanced encryption standards, like AES 256-bit, are commonly employed, making it extremely difficult for cybercriminals to decrypt and access the data without the correct encryption key.
Cloud backup services implement robust access control measures to prevent unauthorized access to the backed-up data. This includes the use of strong authentication methods, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), which adds an extra layer of security by requiring not only a password but also a second form of verification, like a code sent to a mobile device. Such measures ensure that only authorized users can access their data, reducing the risk of identity theft.
Cloud backup providers also frequently adhere to stringent security standards and compliance regulations, such as GDPR in Europe or HIPAA in the United States, which mandate the protection of personal and sensitive information. Compliance with these standards involves regular security audits, penetration testing, and other security practices that strengthen the protection of stored data against breaches that could lead to identity theft.
Regular, automated backups ensure that data is continually updated and preserved in the cloud. In the event of a device being compromised or stolen, the presence of a recent cloud backup means that the individual can quickly restore their personal information to a new device without losing critical data. This capability is particularly important if the original device was compromised in a way that could lead to identity theft, as it allows the individual to maintain access to their personal information and take steps to secure it, such as changing passwords or alerting financial institutions, without delay.
Data integrity features within cloud backups, such as versioning, allow users to revert to earlier versions of their files before they were potentially tampered with. This is crucial in scenarios where data might have been altered or corrupted as part of a cyber attack aimed at facilitating identity theft.
Comparison of Cloud Storage Providers
The following is a list of some of the best cloud storage and backup providers:
2025 Data Sources
- https://www.cisa.gov/sites/default/files/publications/data_backup_options.pdf
- https://www.ready.gov/business/emergency-plans/recovery-plan
- https://www.nccoe.nist.gov/sites/default/files/legacy-files/msp-protecting-data-extended.pdf
- https://www.fbi.gov/contact-us/field-offices/elpaso/news/fbi-tech-tuesday-building-a-digital-defense-to-protect-your-cloud-accounts