A cyber attack is an attempt by an individual or a group to gain unauthorized access to or disrupt the functioning of computer systems, networks, or electronic devices. The purpose of a cyber attack can vary, but it often involves stealing sensitive data, financial information, or intellectual property, as well as causing damage to computer systems or networks.

Types of Cyber Attacks
There are many types of cyber attacks, but here are some of the most common ones:
- Phishing: A type of attack that involves tricking victims into revealing sensitive information such as passwords, credit card details, or personal information. This is often done through a fake email or website that appears to be legitimate.
- Malware: Malware is any software designed to harm or exploit a computer system, and it can take many forms such as viruses, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, or adware.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack: This type of attack aims to overwhelm a system or network with traffic, making it unavailable to users. This is often done using botnets or other methods to flood the network with traffic.
- Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attack: In a MITM attack, the attacker intercepts communication between two parties, allowing them to eavesdrop on the conversation, steal information, or impersonate one of the parties.
- SQL Injection: This type of attack targets databases, where an attacker injects malicious code into a website or application to gain access to sensitive information.
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS): An attack where an attacker injects malicious code into a website or application that then executes on the user’s device, stealing information or executing other malicious actions.
- Advanced Persistent Threats (APT): APTs are long-term targeted attacks that are often carried out by well-funded and highly skilled attackers with specific targets in mind.
These attacks can target individuals, businesses, governments, or other organizations, and can have serious consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and even physical harm. It is important to take steps to protect yourself and your organization from cyber attacks, such as using strong passwords, regularly updating software, and educating yourself and your employees about common cyber threats.
Cyber Attack Survey
What is Phishing?
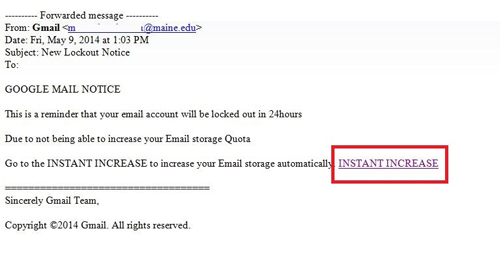
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack in which an attacker attempts to trick the victim into revealing sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, or personal information. This is often done through email or instant messaging, where the attacker will create a fake message or website that appears to be from a legitimate source such as a bank, social media platform, or online retailer.
Phishing attacks often use tactics such as urgent language, threats of account closure, or promises of prizes or rewards to persuade the victim to take action, such as clicking on a link or entering their login credentials. Once the victim provides the requested information, the attacker can use it for various malicious purposes such as identity theft, financial fraud, or other cyber attacks.
Types of Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks vary in sophistication and target, employing social engineering tactics to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security. The primary types include:
- Deceptive Phishing: The most common form, where attackers impersonate a legitimate company to steal personal information or login credentials. Typically, these attacks rely on mass-emailing techniques.
- Spear Phishing: More targeted than deceptive phishing, spear phishing involves personalized messages to specific individuals. Attackers often use information gathered from social media or other sources to increase credibility.
- Whaling: A specialized form of spear phishing that targets high-profile individuals like CEOs or CFOs. Whaling attacks often involve crafting highly sophisticated and convincing emails that appear to be from trusted or high-ranking sources.
- Vishing (Voice Phishing): Conducted via phone calls, where attackers pretend to be from a legitimate organization and attempt to extract sensitive information like credit card details or account passwords.
- Smishing (SMS Phishing): Uses text messages to lure victims into providing personal information or clicking on malicious links.
- Pharming: Redirects users from a legitimate website to a fraudulent one, often by exploiting vulnerabilities in DNS (Domain Name System) servers. Unlike other phishing attacks, pharming doesn’t require baiting the victim with a deceptive message.
- Clone Phishing: Involves creating an almost identical replica of a legitimate message that a user has already received, but with malicious links or attachments.
- Angler Phishing: Utilizes social media platforms to mimic customer service accounts and reach victims, tricking them into handing over personal information or login credentials.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): A sophisticated scam targeting businesses working with foreign suppliers or businesses that regularly perform wire transfer payments. BEC involves compromising legitimate business email accounts through social engineering or computer intrusion techniques to conduct unauthorized fund transfers.
- Watering Hole Attacks: Targets specific groups by compromising legitimate websites that members of the group are known to visit. The attacker then plants malware on these websites to infect visitors.
Each type of phishing has its nuances and requires tailored security measures for prevention. This includes user education, spam filters, web security solutions, and robust verification processes, especially for sensitive actions like financial transactions or accessing confidential information.
Protective Measures
To protect from phishing attacks, it is important to be cautious and skeptical of any unsolicited emails or messages, especially those that contain urgent or threatening language, or that ask for sensitive information. You should also verify the authenticity of any requests by contacting the company or organization directly through their official website or phone number, rather than through the email or message itself.
What is Malware?
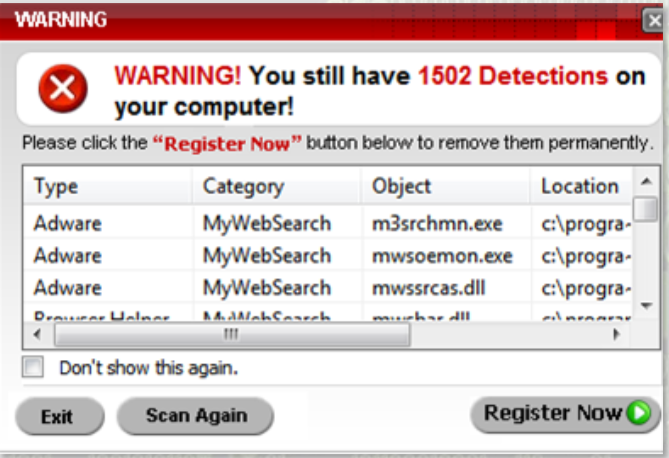
Malware is short for “malicious software”, and it is a type of software that is designed to harm computer systems, networks, or electronic devices. Malware can take many forms and can be spread through various means, such as email attachments, downloads from the internet, or through compromised websites.
Malware can have different purposes, including stealing sensitive data, disrupting computer systems, spying on users, or hijacking computer resources for malicious purposes such as launching attacks on other systems. Examples of malware include viruses, worms, Trojans, ransomware, spyware, and adware.
Types of Malware
Malware encompasses a variety of software types designed to harm, exploit, or unauthorizedly control devices and networks. The primary categories include:
- Virus: Attaches itself to clean files and spreads uncontrollably, altering the way a computer operates and causing damage. It needs a host program to run.
- Worms: Self-replicating malware that spreads across networks without human intervention, often exploiting vulnerabilities in software or operating systems.
- Trojan Horse: Disguises itself as legitimate software. Unlike viruses and worms, it does not replicate itself, but it can deliver a payload like a virus or open a backdoor.
- Ransomware: Encrypts the victim’s data and demands payment for the decryption key. High-profile variants like WannaCry and Petya have caused significant disruption.
- Spyware: Covertly collects information about a person or organization without their knowledge. It often gathers sensitive information like login credentials.
- Adware: Automatically delivers advertisements. While not always harmful, it can be intrusive and may come bundled with spyware.
- Rootkits: Gives cybercriminals administrator-level access to a victim’s system. They are hard to detect because they are activated before a system’s operating system has completely booted up.
- Keyloggers: Records the keystrokes made on a computer to steal passwords or other sensitive information.
- Botnets: Networks of infected devices, called bots, controlled as a group without the owners’ knowledge, often used for Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks.
- Logic Bombs: Triggered by specific conditions, such as a date or the deletion of an employee’s account. Once activated, they can perform malicious actions like deleting files or corrupting data.
Each type of malware has unique characteristics and requires different mitigation and prevention strategies. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) often use a combination of these types to infiltrate and remain in a target network undetected for long periods. Cybersecurity measures like firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems, along with regular software updates and user education, are crucial in defending against these threats.
Protective Measures
To protect against malware, it is important to use antivirus and antimalware software, keep software and operating systems up to date, avoid clicking on suspicious links or opening suspicious email attachments, and regularly back up important data.
What is a Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack?
A Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack is a type of cyber attack that aims to make a website, network, or online service unavailable to its intended users by overwhelming it with traffic or other types of requests. In a DoS attack, the attacker sends a large volume of traffic to the target system, with the intention of consuming its resources such as bandwidth, processing power, or memory, which can cause it to crash or become unresponsive.
DoS attacks can be carried out using various methods, such as flooding the target with traffic from multiple sources, sending malformed packets or requests that cause the system to crash, or exploiting vulnerabilities in the target’s software or network infrastructure.
The goal of a DoS attack is often to disrupt the target’s normal operations, prevent access to its services, or to cause reputational damage. In some cases, DoS attacks can be used as a smokescreen to distract security personnel while another attack is carried out.
Protective Measures
To defend against DoS attacks, organizations can use various techniques such as network segmentation, load balancing, and traffic filtering to mitigate the impact of such attacks. However, sophisticated DoS attacks can be difficult to detect and mitigate, making it important to have a comprehensive incident response plan in place.
What is a Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attack?
A Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack is a type of cyber attack where an attacker intercepts communication between two parties, allowing them to eavesdrop on the conversation, steal information, or impersonate one of the parties. In a MitM attack, the attacker positions themselves between the two parties, relaying messages between them, while also intercepting and modifying the messages as they pass through.
MitM attacks account for 35% of WiFi exploitation activity.
MitM attacks can be carried out on various communication channels, including email, instant messaging, and voice calls, as well as web-based communication such as online banking or shopping. MitM attacks can be conducted using various techniques, including phishing, malware, or exploiting vulnerabilities in network infrastructure.
The goal of a MitM attack is often to steal sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card numbers, or personal information, or to perform actions on behalf of the victim, such as transferring money or making unauthorized purchases.
Protective Measures
To protect against MitM attacks, it is important to use secure communication channels such as encrypted messaging or SSL/TLS-protected websites, to use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication, and to avoid using public Wi-Fi or other unsecured networks when accessing sensitive information. It is also important to keep software and operating systems up to date, and to be cautious of any suspicious activity or requests for sensitive information.
What is a SQL Injection?
A SQL injection is a type of cyber attack that targets databases, where an attacker injects malicious code into a website or application to gain access to sensitive information stored in the database. In a SQL injection attack, the attacker sends specially crafted input to the application, which is not properly sanitized or validated, allowing the attacker to execute arbitrary SQL commands on the database.
Once the attacker gains access to the database, they can steal sensitive information such as user credentials, financial data, or personal information, or modify, delete or insert data into the database for malicious purposes.
SQL injection attacks are a common attack vector for web applications that interact with databases, and can be carried out using various techniques such as blind SQL injection, error-based SQL injection, or union-based SQL injection.

Protective Measures
To protect against SQL injection attacks, it is important to use secure coding practices such as parameterized queries or stored procedures, to validate and sanitize user input, and to limit the privileges of database users to reduce the impact of a successful attack. It is also important to keep software and operating systems up to date, and to monitor database activity for signs of suspicious activity.
What is Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)?
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) is a type of cyber attack where an attacker injects malicious code into a website or web application that is then executed on the user’s device, allowing the attacker to steal sensitive information or perform other malicious actions. In an XSS attack, the attacker sends a specially crafted input to the website, which is not properly validated or sanitized, allowing the attacker to inject their own code into the website.
Once the code is executed on the user’s device, it can be used to steal sensitive information such as login credentials or financial data, or to perform other malicious actions such as redirecting the user to a fake website or performing unauthorized actions on the user’s behalf.
XSS attacks can be carried out using various techniques, such as reflected XSS, where the injected code is immediately returned in the server’s response to the user’s input, or stored XSS, where the injected code is stored in the website’s database and executed whenever the user views the affected page.
Protective Measures
To protect against XSS attacks, it is important to use secure coding practices such as input validation and output encoding, to sanitize user input, and to limit the use of user-generated content on websites or web applications. It is also important to keep software and operating systems up to date, and to monitor website activity for signs of suspicious activity.
What are Advanced Persistent Threats?
Advanced Persistent Threats (APT) are a type of cyber attack that are characterized by their long-term and targeted nature. APTs are carried out by highly skilled and well-funded attackers, who are often sponsored by nation-states or criminal organizations, with the goal of gaining access to sensitive information, intellectual property, or other valuable assets.
APTs are carried out in multiple stages, with the attacker gaining a foothold in the target’s network or system, and then moving laterally to other systems to establish persistent access. The attacker then uses various techniques, such as data exfiltration, keylogging, or remote control, to steal sensitive information or carry out other malicious actions.
APTs are often carried out using social engineering techniques, such as spear-phishing or pretexting, to gain access to the target’s systems or network. APTs are also characterized by their use of custom-made or zero-day malware, which can evade detection by traditional antivirus software and security controls.
Protective Measures
To defend against APTs, it is important to use a multi-layered approach to security, including perimeter defenses, network segmentation, access controls, and endpoint protection. It is also important to use threat intelligence and security analytics to detect and respond to potential APT attacks, as well as to train employees on how to recognize and avoid social engineering tactics.
2025 Data Sources