NordVPN

Best VPN Overall
- AES-256 encryption
- Over 7,00 servers
- 30-day risk-free trial period
Surfshark

Best VPN for Mobile
- AES-256-GCM encryption
- Over 3,200 servers
- Unlimited connections
CyberGhost

Best No Logs Policy
- AES 256-bit encryption
- Over 7,400 servers
- Strict no-logs policy
Nowadays, most of our information lives on the web. If you’re working from home or in a public space, such as your local coffee shop, you need an extra layer of security to keep your data and interests safe from hackers. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) give protection by encrypting your online data and ensuring your online anonymity. The following are the best VPNs for keeping you safe online.
The 3 Best VPNs of 2025
- NordVPN – Best VPN Overall
- Surfshark – Best VPN for Mobile Devices
- CyberGhost – Best No Logs Policy
NordVPN – Best VPN

NordVPN has top-of-the-line encryption and more than 7,000 servers. Customers have a verified “no-logs” policy to keep browsing and information private. Other popular features include worldwide access to all streaming services without blocking, advanced encryption to protect your browsing data, and peer-to-peer (P2P) capabilities to share files securely. Best of all, NordVPN masters streaming videos with its SmartPlay feature using DNS technology and NordVPN’s apps.
NordVPN is considered one of the best VPNs due to several factors:
- Strong security features: NordVPN uses AES-256 encryption, which is currently one of the most secure encryption methods available. It also offers additional security features such as double VPN, Onion over VPN, and CyberSec.
- Large server network: NordVPN has a vast network of over 7,000 servers located in 118 countries. This extensive network allows users to connect to servers in different locations worldwide and access geo-restricted content.
- User-friendly interface: The NordVPN app has a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate, making it simple for users to connect to a server and start using the VPN.
- No-logs policy: NordVPN has a strict no-logs policy, meaning that they do not store any user data, ensuring that users’ online activity remains private.
- Competitive pricing: NordVPN offers competitive pricing for its service, making it an affordable option for those looking for a reliable VPN.
NordVPN has established itself as a leading virtual private network (VPN) provider, renowned for its robust security features, extensive server network, and user-friendly interface. In this review, we delve into its key aspects to help you determine if it’s the right choice for your online privacy needs.
Security and Privacy
NordVPN employs AES-256 encryption, the industry standard for securing data transmissions. Its strict no-logs policy ensures that user activities are not recorded, bolstered by its Panama jurisdiction, which is outside the purview of data-sharing alliances like the Five Eyes. Additional security features include a kill switch to prevent data leaks if the VPN connection drops, and specialty servers such as Double VPN and Onion Over VPN for enhanced privacy.
Server Network and Performance
With over 7,000 servers in 118 countries, NordVPN offers a vast network that facilitates reliable and speedy connections. This extensive coverage ensures users can access content globally with minimal latency. Performance tests indicate that NordVPN maintains high-speed connections suitable for streaming, gaming, and torrenting activities.
Streaming and Torrenting
NordVPN excels in bypassing geo-restrictions, allowing access to various streaming platforms such as Netflix, Hulu, and BBC iPlayer. For torrenting enthusiasts, NordVPN provides dedicated P2P servers optimized for secure and efficient file sharing.
User Experience and Support
The NordVPN application is intuitive, supporting multiple platforms including Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and iOS. Users can connect up to ten devices simultaneously under a single account. Customer support is available 24/7 through live chat and email, ensuring assistance is readily accessible.

Pricing
NordVPN offers several subscription plans that vary in price depending on the subscription duration and the features desired:
- Monthly Plan: $12.99 – $17.99 per month
- One-Year Plan: $59.88 – $119.88 annually
- Two-Year Plan: $81.36 – $201.36 biennially
You have the option of picking between the following plans:
- Prime Plan
- Complete Plan
- Plus Plan
- Basic Plan
Pros and Cons
Pros
- Robust security features with advanced encryption
- Extensive global server network
- Strong performance with high-speed connections
- Effective in unblocking geo-restricted content
Cons
- Premium pricing compared to some competitors
- Limited to ten simultaneous device connections
Summary
NordVPN stands out as the best VPN service this year, offering comprehensive security features, a vast server network, and reliable performance. While it comes at a premium price point, it reviewed very well and the robust privacy protections make it a worthwhile investment for users seeking a dependable VPN solution.
Surfshark – Best VPN for Mobile Devices

Surfshark is one of the most popular VPN options, especially for Android users. You’ll be free of hacking, malware, identity theft, and ads based on your browsing history.
Surfshark is considered one of the best VPNs due to several factors:
- Strong security features: Surfshark uses AES-256-GCM encryption, which is a highly secure encryption method, and also offers additional security features such as multi-hop VPN, ad-blocking, and malware protection.
- Large server network: Surfshark has a global network of over 3,200 servers in more than 65 countries, allowing users to access geo-restricted content from around the world.
- Unlimited simultaneous connections: Surfshark allows users to connect an unlimited number of devices to their VPN service with a single account, making it an excellent choice for families or individuals with multiple devices.
- No-logs policy: Surfshark has a strict no-logs policy, ensuring that users’ online activity remains private and secure.
- Competitive pricing: Surfshark offers affordable pricing for its service, especially considering the high level of security and the number of features it provides.
Surfshark has rapidly emerged as a prominent player in the VPN market, offering a blend of robust security features, user-friendly design, and exceptional value. Launched in 2018, it has garnered attention for its commitment to user privacy and innovative functionalities.
Security Standards
At the core of Surfshark’s offerings is its strong emphasis on security. The service employs AES-256-GCM encryption, a standard renowned for its resilience against cyber threats. Users can choose from multiple VPN protocols, including OpenVPN, IKEv2, and the high-speed WireGuard, ensuring a balance between security and performance.

A standout feature is the CleanWeb suite, which effectively blocks ads, trackers, and malicious websites, enhancing the overall browsing experience. Additionally, the MultiHop function allows users to route their connection through multiple servers, adding an extra layer of anonymity.
Performance
Surfshark boasts a network of over 3,200 servers across 100 countries, providing users with extensive global coverage. In performance tests, Surfshark consistently delivers impressive speed test results with consistent performance and advanced security features. This makes it suitable for data-intensive activities like streaming high-definition content and online gaming.
User Experience
The user interface is intuitively designed, catering to both VPN novices and seasoned users. The main dashboard offers a straightforward connection process, while advanced settings are easily accessible for those seeking customization. Surfshark allows unlimited simultaneous device connections, a feature that sets it apart from many competitors.
Features
Beyond standard VPN capabilities, Surfshark offers a suite of supplementary tools. The Whitelister feature enables split tunneling, allowing specific apps or websites to bypass the VPN. The GPS spoofing function is particularly useful for mobile users, aligning the device’s GPS location with the connected VPN server.
For users concerned about data breaches, Surfshark Alert provides real-time monitoring, notifying them if their personal information is compromised. The Surfshark Search tool offers a private, ad-free search experience, ensuring queries remain confidential.
Pricing Plans
Surfshark’s pricing structure is competitive, especially for long-term commitments. While the starting monthly plan is priced at $15.45, opting for extended subscriptions significantly reduces the monthly cost, making it an economical choice for budget-conscious users. You also have the option of picking up the Surfshark One suite for $17.95 per month which offers private search features, data leak alerts, and additional security products on top of their VPN offering. The following is a high-level breakdown of pricing:
- Monthly Plan: $15.45 – $20.65 per month
- One-Year Plan: $47.85 – $91.35 annually
- Two-Year Plan: $59.13 – $115.83 biennially
You have the option of picking between the following plans:
- Surfshark Starter
- Surfshark One
- Surfshark One+

Summary
Surfshark presents a compelling VPN solution that combines strong security measures, high performance, and a wealth of features at an attractive price point. This is why it landed in our second spot for the best VPN during our review. NordVPN only slightly beat it out due to its total number of servers (7,205 vs 3,200).
CyberGhost – Best No Logs Policy

CyberGhost gives you everything you need in a VPN with a “No-Logs” Policy, AES 256-bit encryption, an automated kill switch, and unlimited bandwidth. It also offers 24/7 customer service and 6,800 VPN “NoSpy” in-house servers to stay safe in 88 countries. CyberGhost lets you hide your IP address and use one of theirs for better browsing security. Mac users are fond of the company because it is committed to security and privacy with its traffic encryption when using public WiFi networks.
CyberGhost VPN is a popular choice for users looking for robust online privacy, reliable security features, and a user-friendly experience. With an expansive server network, straightforward applications, and competitive pricing, it caters to a wide audience, from casual browsers to avid streamers and torrenters.
Security Features
CyberGhost takes security seriously, utilizing AES-256 encryption to ensure top-notch protection for user data. It includes key privacy features such as an automatic kill switch, DNS leak protection, and a strict no-logs policy. These features help ensure that user activity remains private, even in the event of unexpected disconnections. Based in Romania, outside of the 14 Eyes surveillance alliance, CyberGhost benefits from a jurisdiction that prioritizes user privacy.
CyberGhost boasts an extensive server network, with over 9,200 servers in more than 100 countries. This vast selection ensures users have access to fast, reliable servers worldwide. Performance is solid, with minimal speed loss during streaming, downloading, or general browsing. Its integration of the WireGuard protocol enhances connection speed and stability.
CyberGhost excels in bypassing geo-restrictions, making it a favorite among streaming enthusiasts. Dedicated servers optimized for platforms like Netflix, Hulu, and Disney+ ensure smooth, buffer-free streaming. For torrenting, CyberGhost provides P2P-optimized servers that enable safe and efficient file sharing.
The VPN offers user-friendly apps for Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and even Linux, ensuring accessibility across devices. The apps are intuitively designed, making them suitable for beginners while still providing advanced settings for tech-savvy users. CyberGhost allows up to seven simultaneous device connections per account, which is enough for most households.
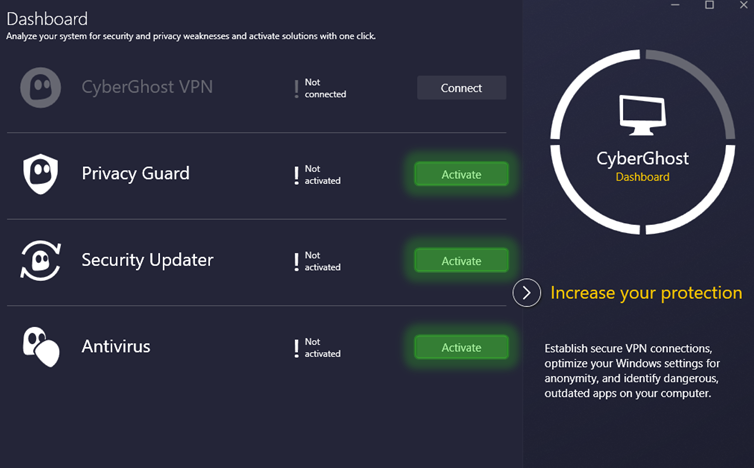
CyberGhost includes a built-in ad and malware blocker, split tunneling (on certain platforms), and smart rules for customizing your VPN experience. It also offers NoSpy servers, designed for enhanced privacy and located in Romania, which are managed entirely in-house.
Pricing and Plans
CyberGhost has the most simple and easiest to understand pricing options when compared to NordVPN and Surfshark. The following is the plan structure for CyberGhost which has varying pricing based only on plan duration and not features:
- Monthly Plan: $12.99 per month
- One-Year Plan: $41.94 every 6 months
- Two-Year Plan: $56.94 for the first 2 years
Pros and Cons
Pros
- Extensive global server network
- Optimized servers for streaming and torrenting
- Strong security and privacy features
- User-friendly apps across multiple platforms
- Affordable long-term plans with a 45-day money-back guarantee
Cons
- Limited simultaneous device connections (7)
- Split tunneling not available on all platforms
Summary
CyberGhost VPN offers an impressive combination of security, speed, and user-friendliness, making it an excellent option for both beginners and advanced users. Its optimized servers for streaming and torrenting, coupled with robust privacy features, provide a versatile experience that can meet a variety of needs. While some minor drawbacks, such as the device connection limit, might affect larger households, its overall performance and value make it a standout choice in the VPN market.
Honorable Mentions
The following are some of the other VPNs we tested and reviewed for our best VPN list but fell out of our top 3 picks.
- ExpressVPN
- Private Internet Access
- TunnelBear
- IPVanish
- Hotspot Shield
- TotalVPN
What is a VPN?

When a user connects to a VPN, their internet traffic is routed through an encrypted tunnel, which protects the user’s data from being intercepted or monitored. This makes it more difficult for anyone to access the user’s online activities or personal information, including their IP address, location, and browsing history.
VPNs can also be used to bypass geographical restrictions or censorship, allowing users to access content that may be restricted in their country or region. Businesses and organizations often use VPNs to provide their employees with secure remote access to company resources and data.
The Best VPN Features to Consider
If you’re looking for the best VPN for your needs, you’ll want to have a few top features whether you’re working, shopping, or streaming.
- The number of servers: The more servers a VPN has, the better. A high number of servers gives customers better upload and download speeds because one server won’t be too crowded. Keep in mind that the more servers a company has, the more expensive maintenance is for the company, so subscription costs tend to scale up with server count.
- Available platforms: Before you decide which VPN you want to use, it’s essential to make sure it works with your preferred platforms. You can find out by checking the VPN’s website or asking the customer support team. You’ll also want to make sure the VPN has a browser extension and mobile app to connect to your mobile device conveniently.
- The number of connected devices: If you have a family, you’ll want something with a high number of simultaneously connected devices to cover gaming consoles, laptops, tablets, smartphones, and more if needed.
VPN stands for Virtual Private Network. It is a secure and encrypted connection between a computer or device and the internet. VPNs are often used to protect the user’s online privacy and security by creating a private network connection that encrypts all traffic between the user’s device and the internet. This helps to prevent eavesdropping, hacking, and other online threats.
How do VPNs Work?
VPNs function by creating a secure, encrypted tunnel between a user’s device and a remote VPN server. This process begins when the VPN software on the user’s device establishes a connection to the VPN server, using protocols such as OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec, or IKEv2, among others. These protocols are responsible for the secure transmission of data across the internet, ensuring that all data sent and received is encrypted and thus unreadable to anyone who might intercept it.
Encryption plays a crucial role in the functioning of VPNs. It involves converting the original data into an encoded version that can only be decrypted with the correct encryption key. This ensures that even if the data is intercepted, it cannot be deciphered by unauthorized parties. The strength of the encryption is determined by the encryption algorithm and the key length, with AES-256 bit encryption being one of the most secure options available today.
Once the encrypted tunnel is established, the user’s internet traffic is routed through the VPN server. This means that to any external observer, such as websites or online services, the user appears to be accessing the internet from the IP address of the VPN server, not their actual location. This not only enhances privacy but also allows users to bypass geographical restrictions and censorship by choosing a server in a different location.
There are 1.5 Billion VPN Users Globally.
DNS requests, which translate domain names into IP addresses, are also routed through the VPN, preventing DNS leaks which could expose the user’s real IP address. Some VPNs implement their own DNS servers to further enhance privacy and security.
Split tunneling is a feature offered by some VPNs that allows users to choose which traffic is routed through the VPN tunnel and which accesses the internet directly. This can be useful for accessing local network resources or reducing VPN usage for applications that do not require enhanced security or privacy.
To maintain security, VPNs often include a kill switch feature that automatically disconnects the user from the internet if the VPN connection drops, preventing data leakage.
The key function of a VPN is to provide a secure and private connection between a user’s device and the internet, while also helping to protect the user’s online privacy and security. The best VPNs offer additional features to ensure you are as protected as possible when connected to the internet.
VPN Uses
- Enhancing online privacy and security: Encrypts internet traffic to protect sensitive data from hackers, especially beneficial on unsecured Wi-Fi networks.
- Circumventing geographical restrictions and censorship: Allows users to access content and services that are blocked or restricted in their region, enhancing freedom of information.
- Maintaining anonymity online: Masks the user’s IP address to prevent tracking of activities and location by websites and advertisers, protecting user identity.
- Securing remote work: Enables safe access to company networks from anywhere, ensuring that sensitive corporate data is transmitted over secure, encrypted connections.
- Avoiding ISP bandwidth throttling: Encrypts data to prevent Internet Service Providers from detecting and slowing down specific types of traffic, ensuring better internet speed and reliability.
- Facilitating secure peer-to-peer (P2P) networking: Provides a secure environment for file sharing and collaboration, crucial for businesses and individuals relying on P2P applications.
- Supporting research and development: Offers access to a broader range of resources and tools, enables collaboration with international colleagues, and allows testing of applications across different network environments.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) serve a multitude of purposes, primarily enhancing online privacy, security, and freedom. They encrypt internet traffic, making it difficult for third parties to intercept or decipher, thus protecting sensitive data from hackers, especially on unsecured Wi-Fi networks like those in cafes or airports. This encryption is vital for safeguarding personal information, login credentials, and financial transactions.
VPNs are also pivotal in circumventing geographical restrictions and censorship. By connecting to servers in different locations, users can access content and services that are restricted or blocked in their own country. This is particularly useful for streaming services, accessing region-locked libraries, and bypassing government censorship to reach blocked websites and platforms.
VPNs are tools for maintaining anonymity. They mask the user’s IP address, making it more challenging for websites and advertisers to track online activities and locations. This anonymity is crucial for journalists, activists, and anyone else concerned with protecting their identity online.
Businesses leverage VPNs to secure remote work. They enable employees to access company networks securely from anywhere in the world, ensuring that sensitive corporate data is transmitted over encrypted connections. This remote access is essential for maintaining productivity and operational continuity, especially in a world that increasingly favors remote and hybrid work models.
VPNs also play a role in network management and optimization. They can help avoid bandwidth throttling by ISPs, a practice where internet speeds are intentionally slowed down. By encrypting the data, VPNs prevent ISPs from detecting and throttling specific types of traffic, such as streaming or large file downloads.
In specialized cases, VPNs facilitate secure peer-to-peer (P2P) networking, allowing users to share files directly and securely. This is significant for businesses and individuals who rely on P2P applications for collaboration or content sharing, providing a secure environment for data exchange.
VPNs contribute to research and development efforts, especially in environments where access to unrestricted internet is necessary for academic or technological advancements. Researchers and developers use VPNs to access a broader range of resources and tools, collaborate with international colleagues, and test applications across different network environments.
Why You Need a VPN
Whether you’re just browsing the web at a coffee shop or handling proprietary data at home, you need a VPN to secure your personal information. Some of the benefits you’ll get:
- Boost security: When browsing or streaming, you shouldn’t have to worry about your data being shared or compromised. VPN encryption keeps your information secure from others.
- Avoid hackers through encryption: Cybercriminals are less likely to access your information when it’s encrypted. They won’t be able to decode your data for their gains.
- Secure passwords, usernames, and bank information: VPNs are great ways to keep your data safe and prevent identity theft.
- Access private networks: A VPN is the safest way to access and share files, data, and applications conveniently.
- Maintain anonymity online: The less information you share on the web, the better. You’ll be able to browse and share without a trace to prevent hacks and cybercrimes.
VPN Device and Operating System Compatibility
- Computers: VPNs can be installed on desktops and laptops running operating systems such as Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Mobile devices: VPNs can be installed on smartphones and tablets running operating systems such as iOS and Android.
- Routers: Some routers come with built-in VPN functionality, which can be used to secure all of the devices connected to the router.
- Streaming devices: Some streaming devices, such as Amazon Fire TV and Apple TV, can be configured to use a VPN connection.
- Gaming consoles: Some gaming consoles, such as the PlayStation 5 and Xbox Series X, can be configured to use a VPN connection.
Windows, macOS, and Linux systems all support VPN connections, with most VPN service providers offering dedicated software for these operating systems. These applications typically provide a user-friendly interface for connecting to VPN servers, adjusting settings, and configuring advanced features like kill switches or split tunneling.
iOS and Android devices, which encompass smartphones and tablets, have native support for VPN connections. This support is twofold: through built-in VPN functionality in the operating system settings and through apps available in the App Store or Google Play Store. These mobile VPN apps are designed to offer a seamless VPN experience on the go, including automatic reconnection features and optimized settings for mobile networks.
Routers can be configured with VPN settings, enabling all devices connected to the router to benefit from the VPN’s security and privacy features. This approach is particularly advantageous for devices that do not natively support VPN software, such as smart TVs, game consoles, and IoT devices. By connecting to a VPN-enabled router, these devices can bypass geographical restrictions and enhance their internet privacy.
Even more specialized devices and operating systems, like Chromebooks running Chrome OS, have support for VPNs. Chrome OS allows users to connect to VPNs through Android apps available on Chromebooks or through native Chrome OS VPN settings, which support several VPN protocols.
As long as a device supports VPN protocols, it can be used with a VPN. It is important to note that some devices may require additional configuration or software installation to use a VPN connection.
Benefits of VPN Use
There are several benefits to using a VPN:
- Enhanced online privacy: When using a VPN, all of the user’s online activities are encrypted and anonymized, meaning that it is more difficult for third parties to track their online activities or identify their IP address.
- Improved online security: VPNs encrypt all of the user’s internet traffic, making it more difficult for hackers or other third parties to intercept or eavesdrop on their online communications.
- Bypassing geographical restrictions: VPNs can be used to access content that may be blocked in certain regions or countries, such as streaming services or social media platforms.
- Accessing restricted networks: VPNs can be used to securely access private or restricted networks, such as those used by businesses or organizations, from remote locations.
- Protection while using public Wi-Fi: VPNs can help protect users from the risks associated with using public Wi-Fi networks, such as the risk of hacking or identity theft.
- Increased anonymity: VPNs can help users remain anonymous online by masking their IP address and location, making it more difficult for others to track their online activities.
VPNs encrypt data transmissions, making it exceedingly difficult for hackers to intercept or decipher information. This is particularly crucial when using public Wi-Fi networks, where vulnerabilities are more pronounced. Encryption standards such as AES-256 provide robust protection against cyber threats, safeguarding personal and financial information.
Privacy is another significant advantage. VPNs mask the user’s IP address and location, making online activities much harder to track by ISPs, government agencies, and advertisers. This anonymization helps protect users’ identities and personal habits from unwanted surveillance and data profiling.
Access to restricted content is a widely appreciated benefit. By changing the apparent location, users can bypass geo-restrictions and censorship, accessing a global internet without barriers. This is essential for users in countries with restricted internet access and for those who want to access region-specific content from streaming services.
VPNs also improve online freedom and anonymity, essential for journalists, activists, and anyone concerned about being monitored. This level of anonymity can protect against targeted attacks and allows for the free exchange of information in restrictive environments.
For remote workers and businesses, VPNs enable secure access to corporate networks and sensitive data from any location. This is vital for maintaining operational security, especially with the increase in remote work, as it extends the office’s security perimeter to anywhere an employee chooses to work.
Network performance and management can also see improvements. While VPNs may sometimes slow down internet speed due to encryption overhead, they can also circumvent ISP throttling based on content type, potentially improving speed for certain services.
VPNs support secure file sharing, allowing users to share and access files over a network without exposing them to the broader internet. This is particularly important for businesses and individuals who require a secure method of file transfer that protects against interception or loss.
VPNs and Identity Theft Prevention
VPNs can help prevent identity theft in several ways:
- Encrypting internet traffic: VPNs encrypt all of the user’s internet traffic, including sensitive information such as login credentials and financial data. This makes it more difficult for hackers or other third parties to intercept or steal this information.
- Masking IP address and location: VPNs hide the user’s IP address and location, making it more difficult for hackers or other third parties to track their online activities or identity.
- Secure Wi-Fi connections: VPNs can help protect users when using public Wi-Fi networks, which are often unsecured and can be easily hacked by identity thieves.
- Avoiding phishing scams: VPNs can help users avoid phishing scams by preventing them from accessing malicious websites that may attempt to steal their login credentials or other sensitive information.
VPNs play a crucial role in identity theft protection by encrypting the data transmitted from a user’s device, ensuring that personal information such as passwords, financial details, and social security numbers are not intercepted or deciphered by cybercriminals. This encryption is especially important when using public Wi-Fi networks, which are notorious for being insecure and a common ground for attackers to steal personal information.
By masking the user’s IP address and routing internet traffic through a secure server, VPNs add an additional layer of privacy, making it difficult for hackers to trace activities back to the user or their device. This anonymity helps protect against targeted phishing attacks, which are often the first step in identity theft.
VPNs also prevent ISPs and websites from tracking user behavior and collecting data without consent. By hiding the user’s online activity, VPNs reduce the risk of identity theft stemming from data breaches or targeted ads based on personal browsing habits and history.
The use of secure and private connections offered by VPNs is vital for online financial transactions. Whether it’s banking, shopping, or any form of e-commerce, VPNs ensure that sensitive financial information is encrypted, drastically reducing the potential for financial fraud and identity theft.
In addition to these protective measures, some VPN providers include advanced security features such as automatic kill switches, which disconnect the internet connection if the VPN drops. This prevents data leakage and ensures that no unsecured data is transmitted, further safeguarding against identity theft.
VPNs also employ DNS leak protection to ensure that all DNS requests are routed through the VPN’s encrypted tunnel, preventing ISPs or potential attackers from viewing the websites a user visits, which could otherwise be used to gather personal information for fraudulent purposes.

James (J.T.) Moore
Systems Engineer and Lead Analyst
2025 Data Sources
- https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/alerts/2021/09/28/cisa-and-nsa-release-guidance-selecting-and-hardening-vpns
- https://www.fdic.gov/regulations/
examiner/it/vpn.html - https://csrc.nist.gov/glossary/term/
virtual_private_network - https://media.defense.gov/2021/Sep/28/
2002863184/-1/-1/0/CSI_SELECTING-HARDENING-
REMOTE-ACCESS-VPNS-20210928.PDF - https://www.nsa.gov/Press-Room/News-Highlights/Article/Article/2791320/nsa-cisa-release-guidance-on-selecting-and-hardening-remote-access-vpns/