Phishing attacks have been on the rise over the years as digital communications methods evolve and expand. Our reliance on text-based communication has made the nation more susceptible to phishing attacks. Let us take a quick look at some facts as to why phishing attacks are a growing problem in the United States.
Phishing Statistics: The Fast Facts
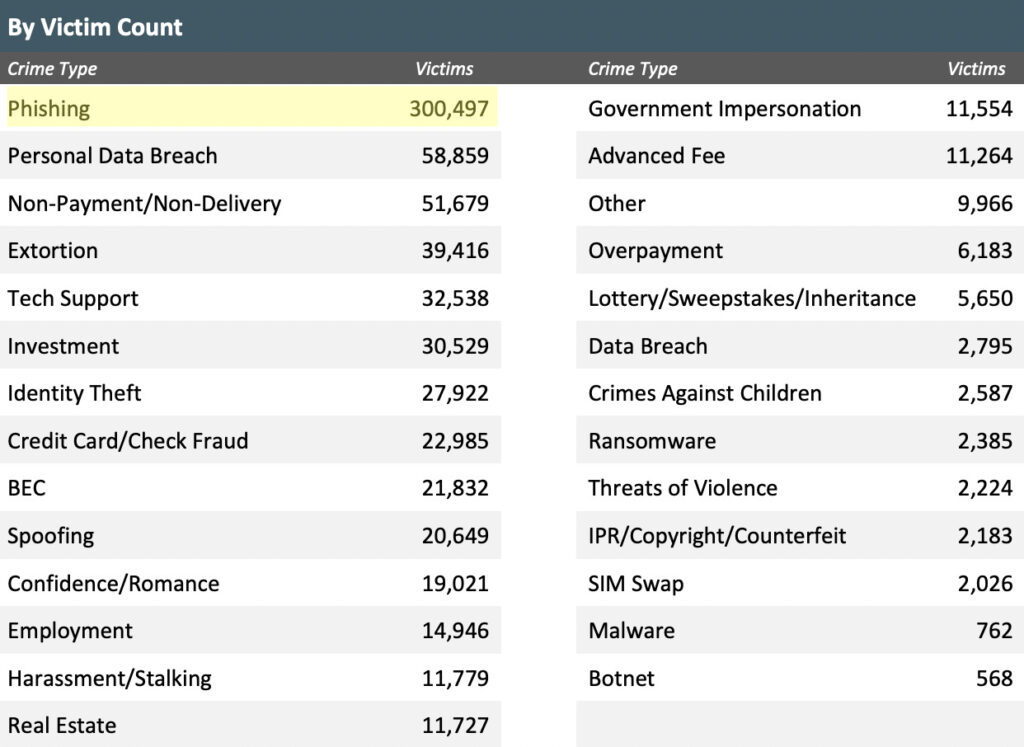
- The IC3 received 300,497 reports of phishing attempts, down from the previous year but up more than 10x since 2018.
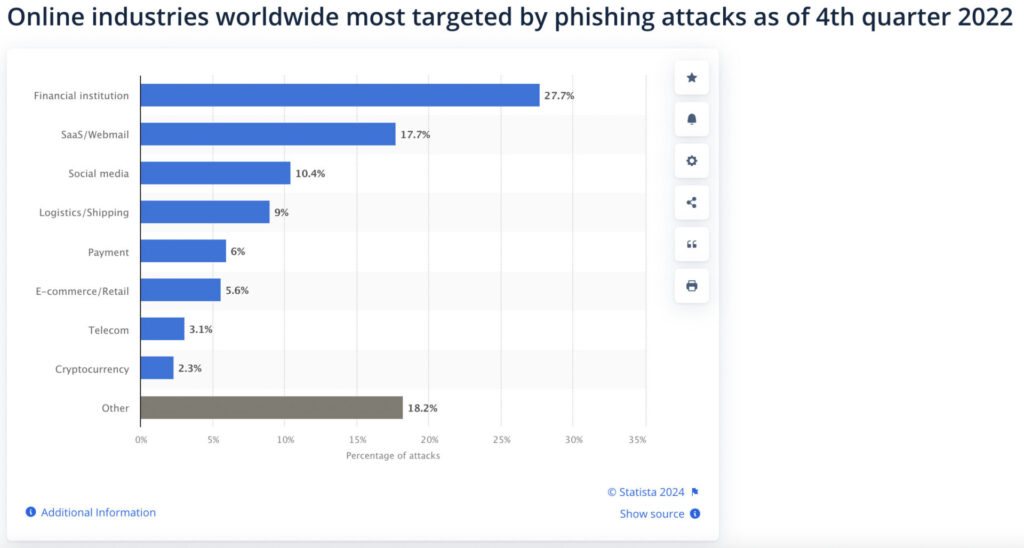
- Financial institutions make up the majority of phishing targets with 27.7% of cases being reported from within this industry
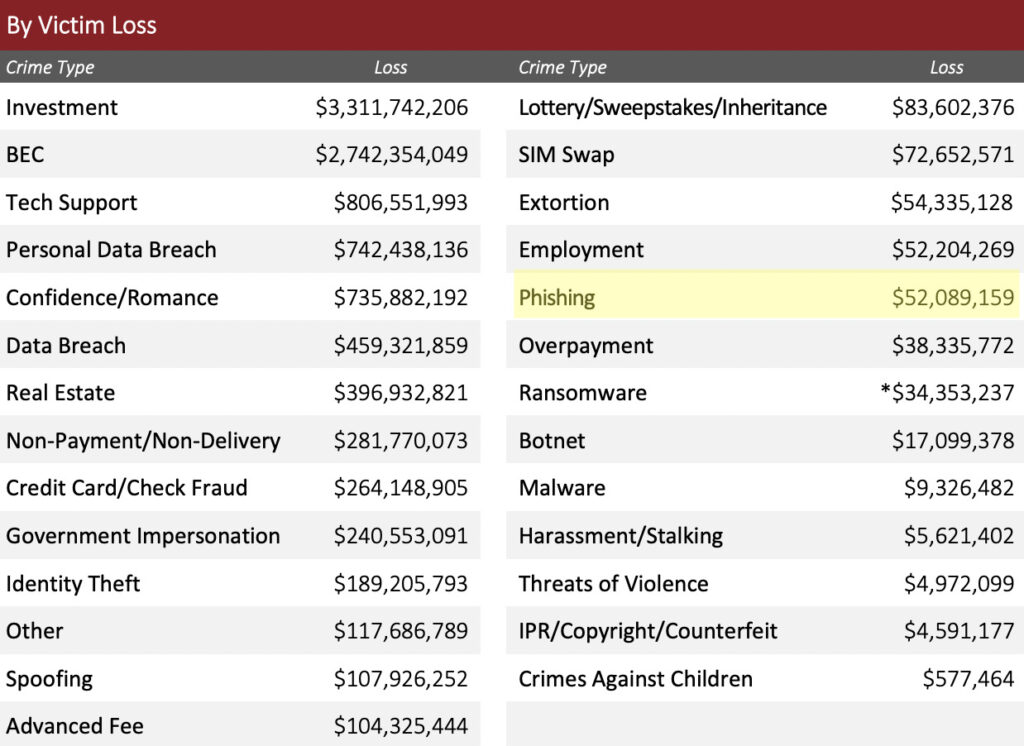
- Total losses from successful phishing attacks was over $52 million
- 91% of phishing attempts are via email
Phishing Statistics, Data, and Facts for 2025
Phishing is becoming more of a threat to both businesses and consumers over the years. The number of victims and losses are growing at a fast rate. Let’s take a look at some of the most standout phishing statistics so far in 2025.
The IC3 Received 300,487 Phishing Reports
The Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) alone received a staggering 300,487 reports phishing attempts. This number was down from the previous year but up greatly since 2018 when they received only 26,379 reports.
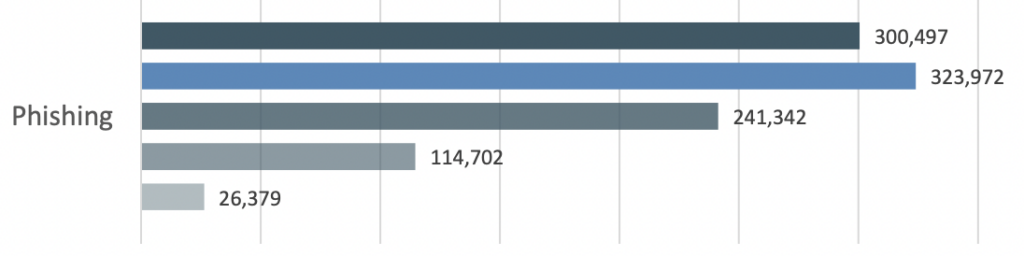
Phishing Attacks Are the #1 Reported Cybercrime
The IC3 received more phishing attack reports than any other cybercrime.
Losses From Known Phishing Attacks Totaled $53 Million
Phishing losses are still on the lower end of the cybercrime scale in terms of losses but have drastically picked up over the years.
91% of Phishing Attacks are Sent Via Email
Email remains the most common method for phishing attacks, with about 91% of all cyberattacks beginning with a phishing email. Of these, 91% are sent via Gmail accounts.
45% of Ransomware Attacks Stem from Phishing
Phishing is the primary method for delivering ransomware, accounting for 45% of all ransomware attacks.
Financial Institutions Are Targeted in 27.7% of Phishing Attacks
Worldwide, the financial sector receives a majority of phishing attacks followed by the SaaS and Social Media industries.
2025 Data Sources
- https://www.ic3.gov/Media/PDF/AnnualReport/2022_IC3Report.pdf
- https://www.cisa.gov/sites/default/files/2023-02/phishing-infographic-508c.pdf
- https://www.ftc.gov/business-guidance/small-businesses/cybersecurity/phishing
- https://www.fbi.gov/contact-us/field-offices/springfield/news/internet-crime-complaint-center-releases-2022-statistics
- https://www.nsa.gov/Press-Room/Press-Releases-Statements/Press-Release-View/Article/3560788/how-to-protect-against-evolving-phishing-attacks/